Research Facilities
The world's most advanced synchrotron radiation facility
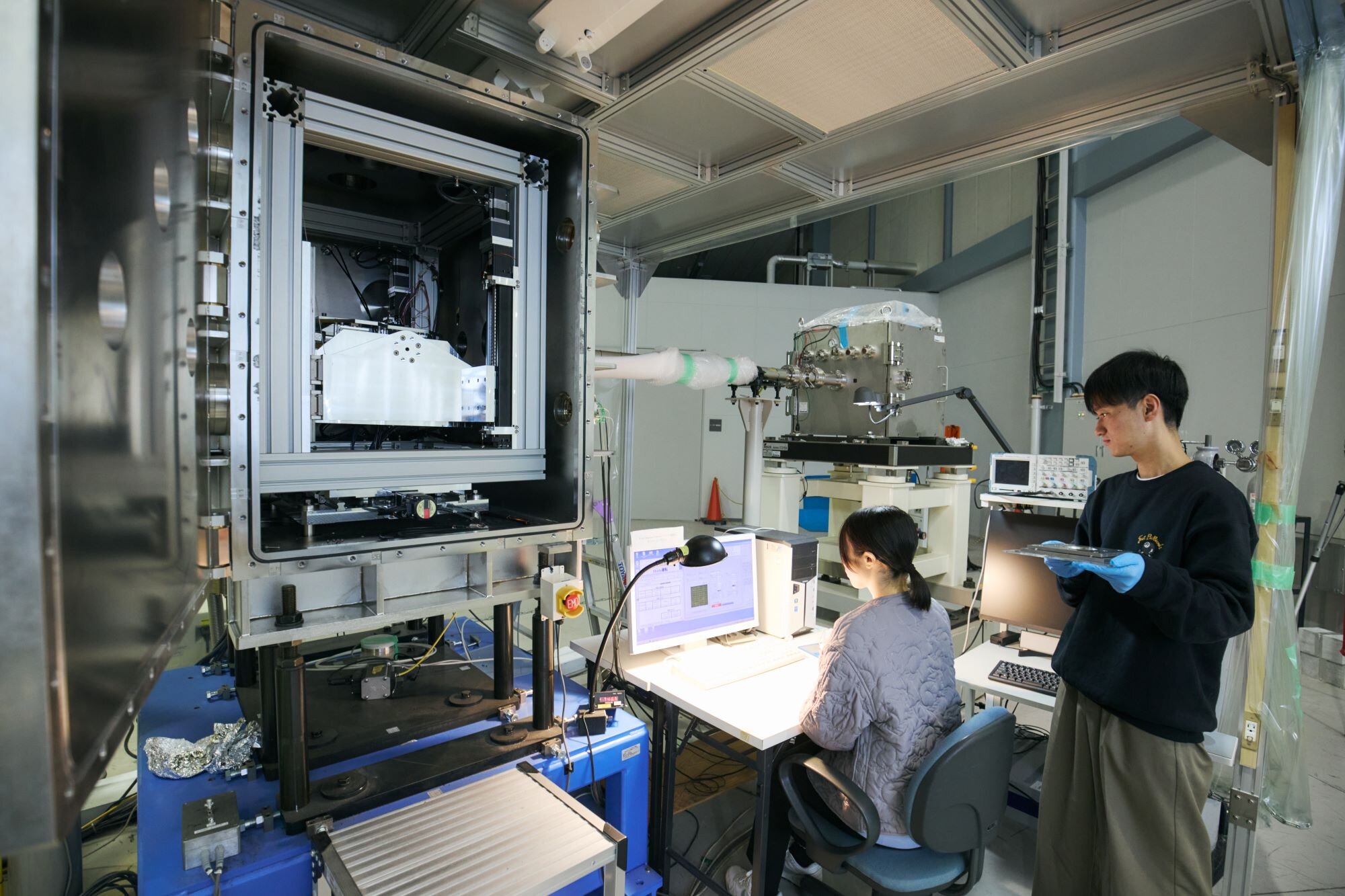
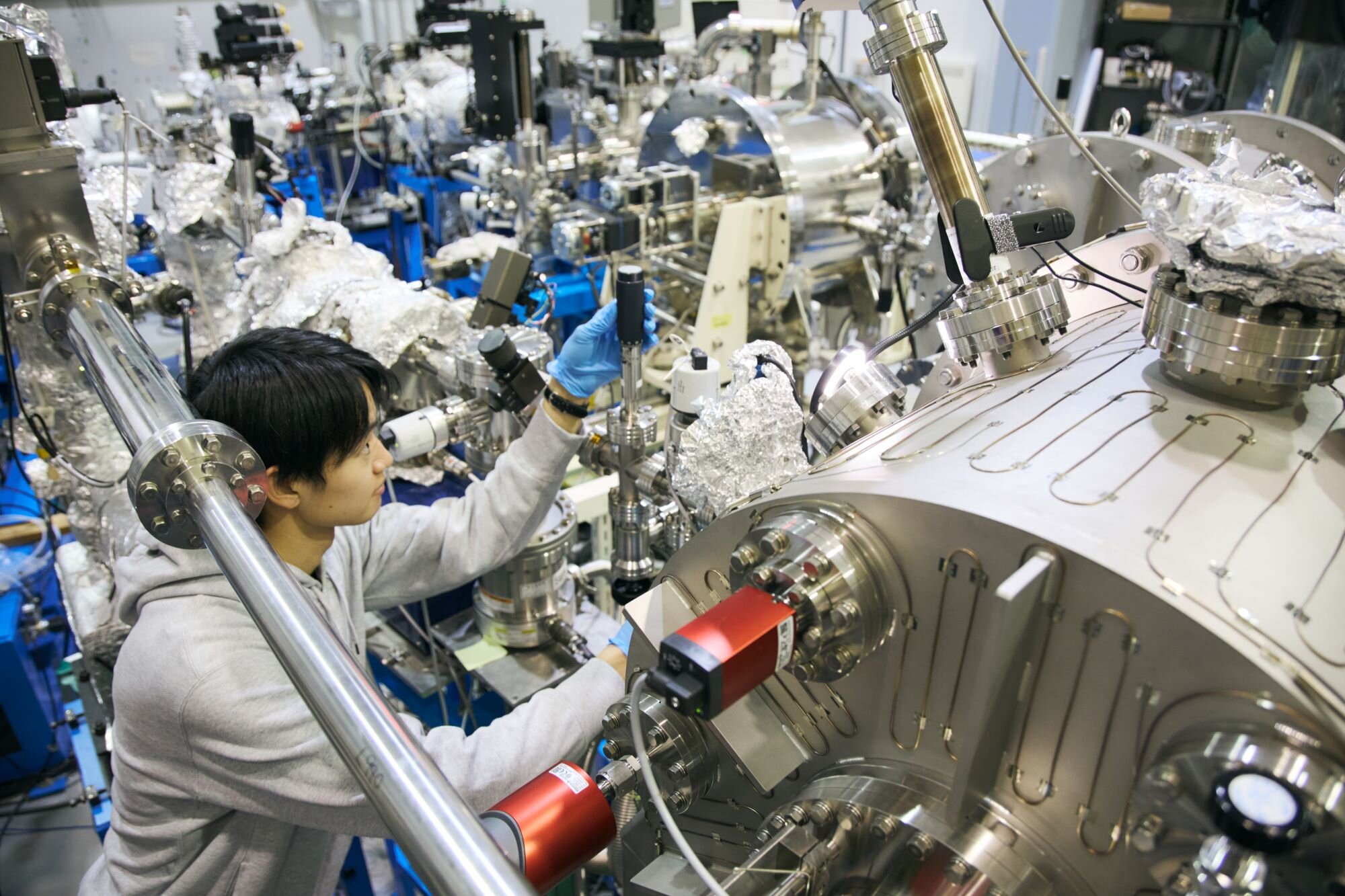
The synchrotron radiation facility "NewSUBARU" operated by the Laboratory of Advanced Science and Technology for Industry is the largest synchrotron radiation facility owned by a university in Japan, and is used in a wide range of fields including ultra-fine processing for semiconductors, medical testing equipment, soft X-ray analysis, and technology development such as new light sources.
Its synchrotron radiation features soft X-rays, which are highly brilliant and 4 to 10 million times brighter than visible light, enabling observation of the structure and electronic state of materials.
In addition to industrial support, NewSUBARU conducts educational activities such as experiments and practical training for students, as well as research in collaboration with the world's leading research facilities such as SPring-8, and SACLA, an X-ray free electron laser facility owned by RIKEN.

Supercomputer that enables large₋scale parallel computations
The Graduate School of Information Science is located on the Kobe Campus for Information Science.
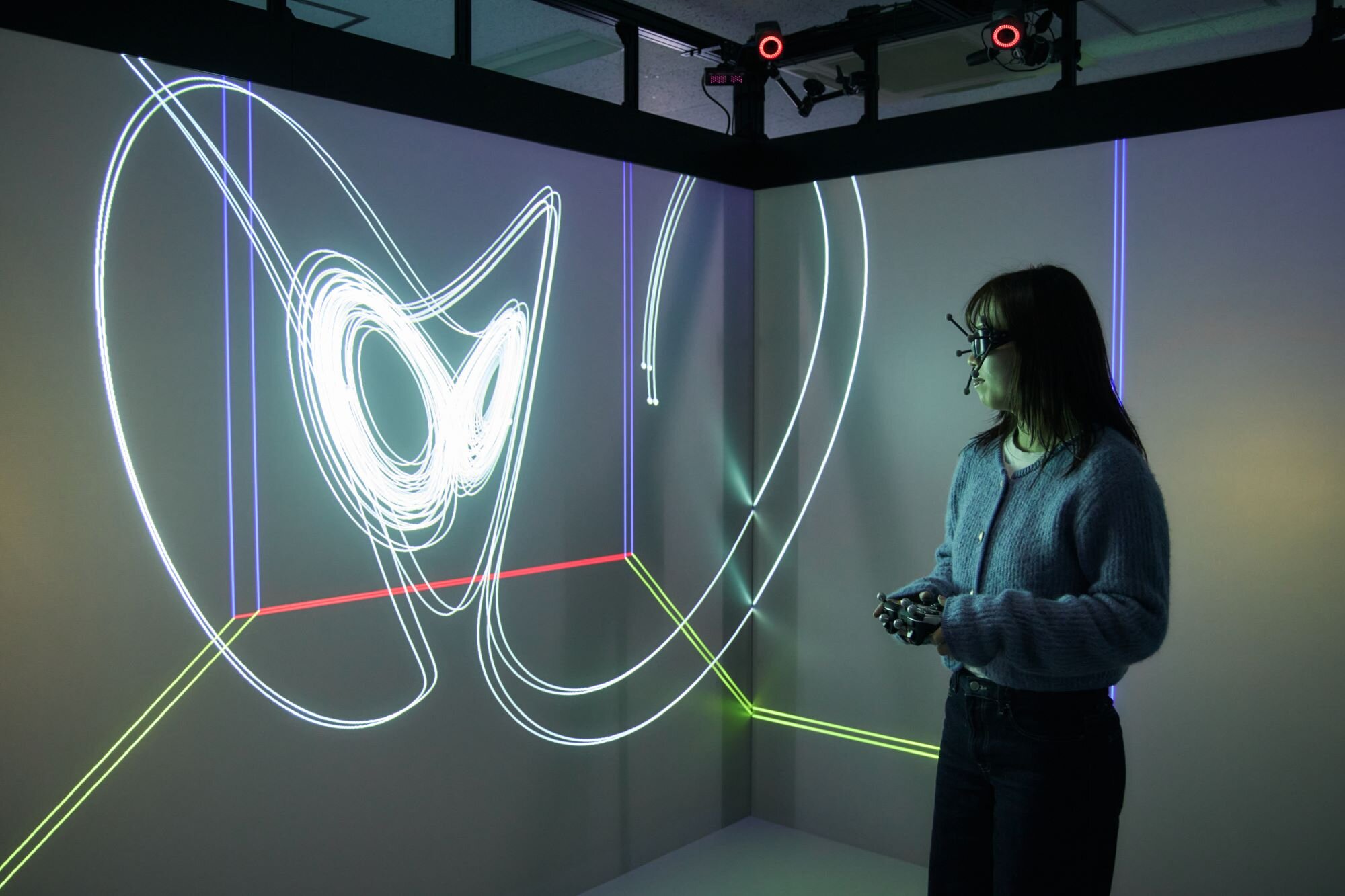
The Data and Computational Science Collaboration Center on the campus has installed a supercomputer which enables large-scale parallel computations, as well as a 3D virtual reality visualization system and tiled displays that enable excellent visualization of the computation results.
Through education and research on the large-scale computation using supercomputers, the Center trains researchers and developers who can utilize supercomputers in various locations, including RIKEN's "Fugaku," which is the world's highest computational power. The fusion of computational science based on simulation science together with data science based on IoT, AI, big data analysis, etc., will contribute to the realization of Society 5.0.


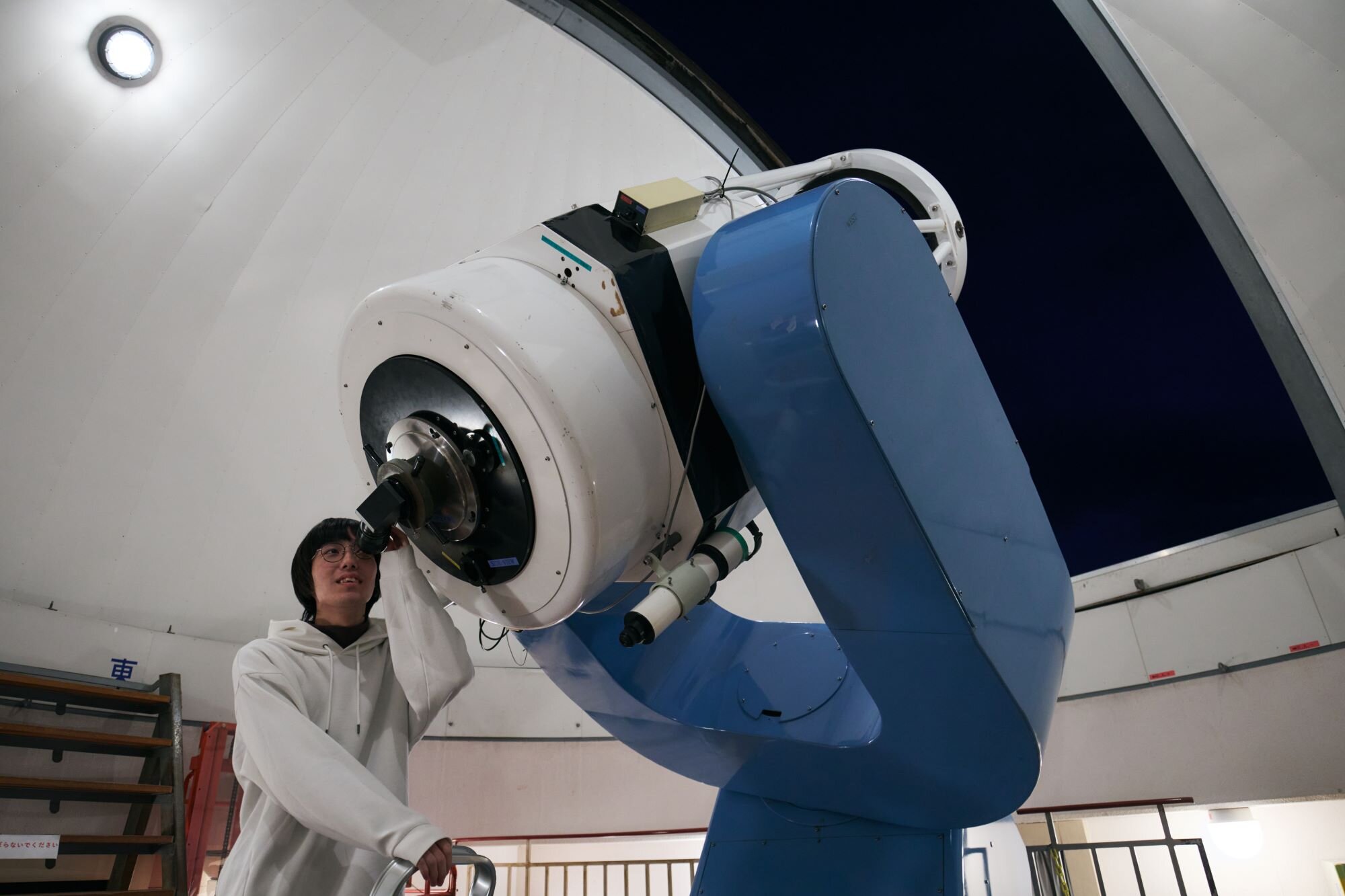
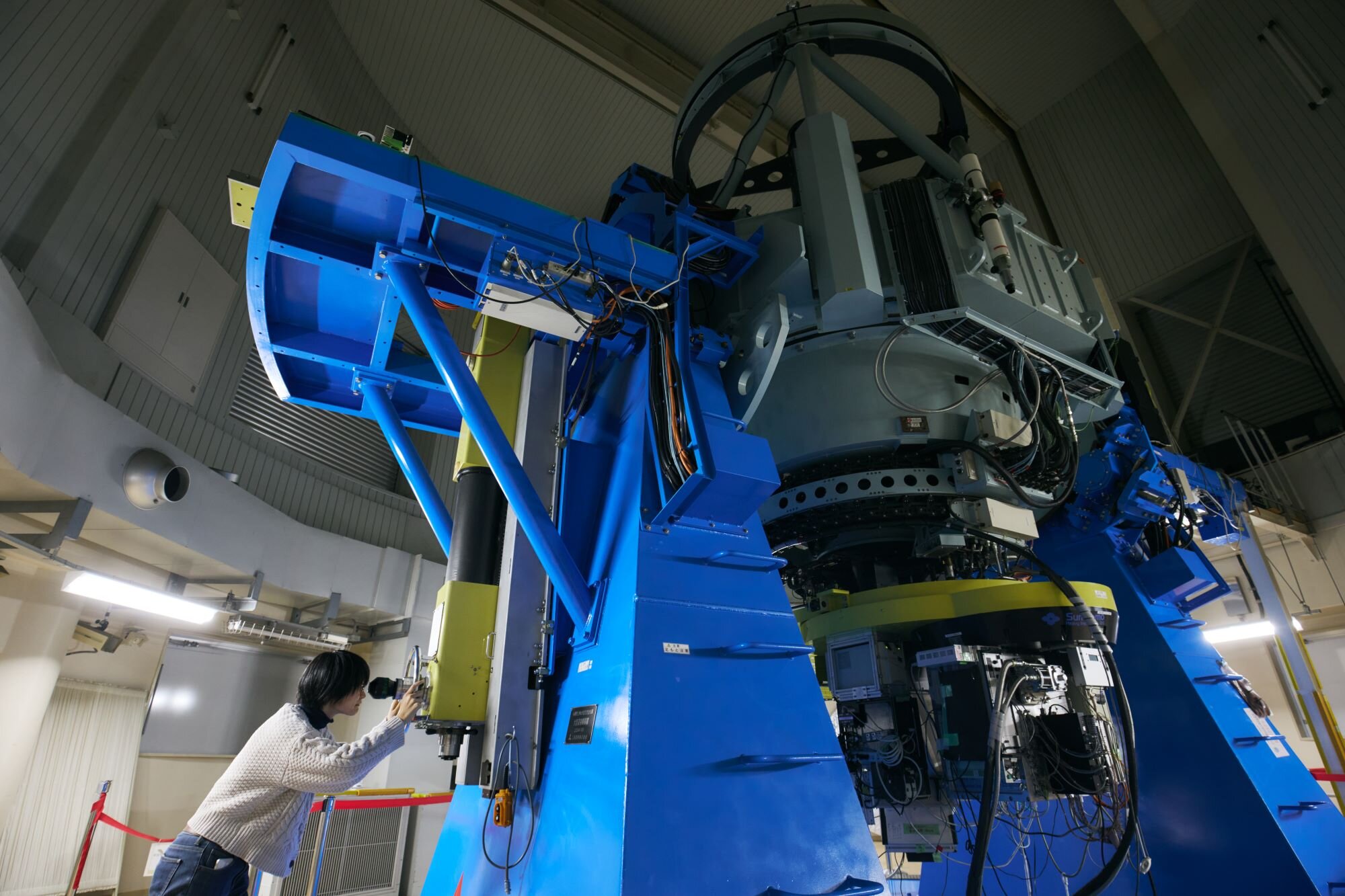
The world's largest telescope for astronomical science
The Nayuta Telescope at Nishi-Harima Astronomical Observatory is one of the world's largest public altazimuth telescopes.
The 2-meter reflector has an aperture about 290 times the diameter of the human eye, or 80,000 times its area, and can observe the Solar system bodies, such as the Moon, Saturn, and Jupiter, as well as stellar cluster and distant galaxies. Visitors can see the realistic appearance of the universe in a large panorama.
Various telescopes owned by Nishi-Harima Observatory, including the Nayuta Telescope, are used for education of astronomical observations and cutting-edge researches on the planets, star formation, nebulae, and galaxies.